Mealworms
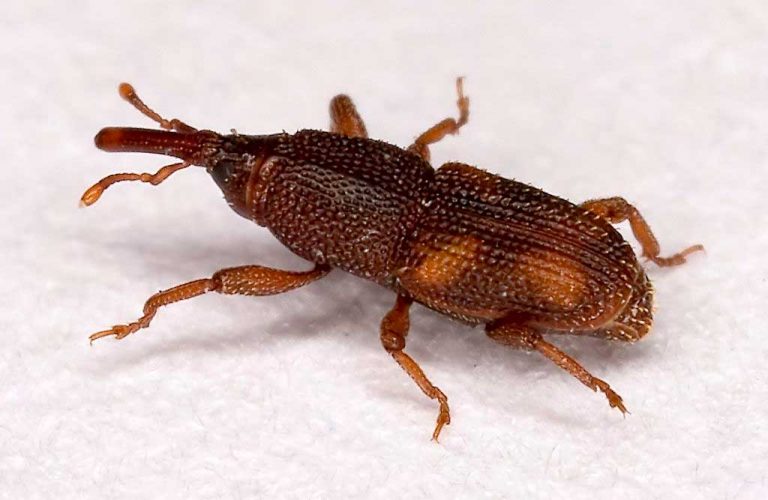
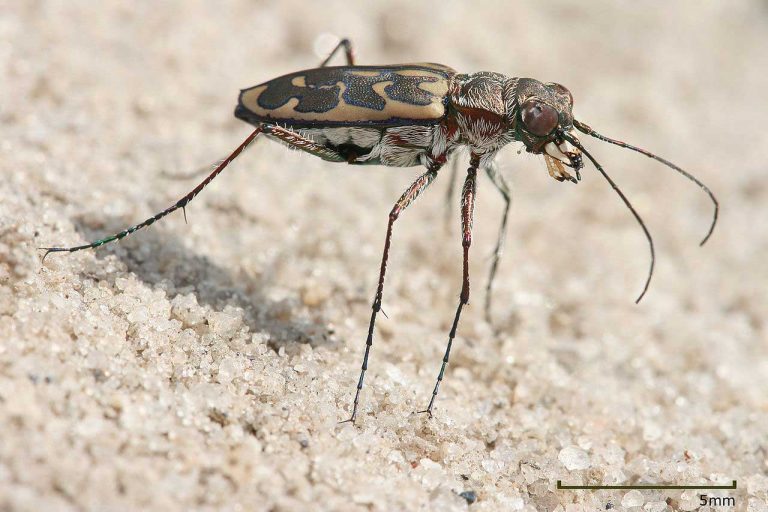
Mealworms are referred to as the larvae of mealworm beetles. Biologically termed Tenebrio Molitor, this beetle belongs to the group of Darkling beetles. Similar to other holometabolic creatures, this beetle to undergoes four stages of the life cycle, namely, egg, larval form, pupal form, and adult beetle form. This mealworm larva attains a size between 1.25 – 1.8 cm.

Reproduction
The breeding pattern of the mealworm is prolific. The mating process of this beetle undergoes a three stage process , namely, the male following the female, overpowering and mounting on the female and then sliding the male aedeaguus inside the female, which releases a packet of sperm. After a few days from mating, the female beetle hides inside the burrows present or made in the soft ground, where she lays more than 500 eggs. Within 4-19 days, the larvae forms appear from the hatched eggs. This egg is a main food of many predators, including many forms of reptiles. This larval form mainly feeds on dead insects and the nearby vegetation. During this stage, the mealworms shed their skin many times. This molting process occurs between every Instar or larvae stage. The larval form of this beetle species undergoes around 9-20 Instars, and after the last one, it transforms into a pupa. In this pupal stage, the mealworm is white in shade, which turns into brown as they mature. Depending on the climatic condition, the pupa will transform into an adult beetle within 3-30 days.
Sex Pheromones
The male mealworm discharges a pheromone of sex, which is used to attract the female for mating. It is found that the odor of this sexual pheromone attracts the female, but the inbreeding in this species causes the attractiveness of this particular pheromones in the males to lessen. Inbreeding reduces the signaling capability in males by increasing the Homozygous deleterious genes leading to unfit males..
Relationship with Humans
The species, Tenebrio Molitor is commonly used in the area of biological research. Its comparatively big size, the status of being a non-model organism and ease of handling and rearing makes it beneficial in studies of proof of concept, in the biochemistry, biology, physiology, evolution and immunology fields.
As a Pest
The records from archives which date back to the Bronze Age referred to mealworms as human pests. While the later findings from British isles and northern Europe mentions that, it is not visible in the records from the ancient Egypt.
As a Food

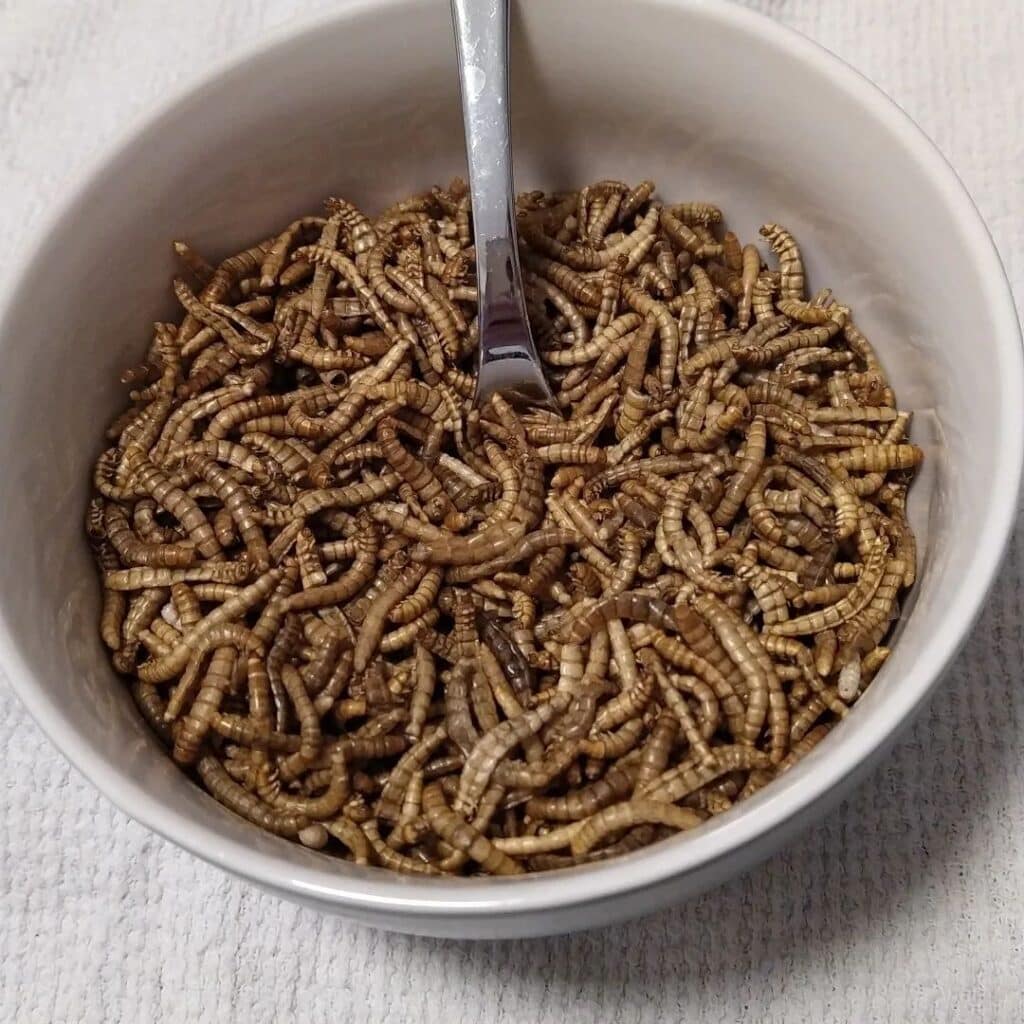
Mealworms – Photo by: Peter Halasz
Entomophagy suggests that mealworms form an integral part of the Chinese cuisine. They are fit to be eaten by humans. Mealworms whether fried or baked are promoted as a nutritious snack. With a humid source such as sliced potato, carrots or apple they can be nurtured on fresh oats, wheat bran or grain with much ease.
New tequila flavoured candies are made rich with mealworms. The moth Hypopta Agavis’s larva is normally used as the “tequila worm” in some mescals(Wiki- a distilled alcoholic beverage made from the maguey plant that is a form of Agave), since mealworms were not available in tequila from ancient times.
The uses of mealworms ranges from being used as a fodder for pet animals like fish, reptiles,and birds to being used as a fishing bait at times. During the nesting season, wild birds present in bird feeders are also fed with mealworms. They are known for their protein rich content.
They are in the market widely in oatmeal or bran containers..For keeping the mealworm in its larval stage and attaining an unusual length of 2cm or more, a juvenile hormone is added to its fodder by the mealworm growers for commercial use.

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.