Zebra Mice
Scientific Classification
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Subfamily: | Murinae |
| Genus: | Lemniscomys |
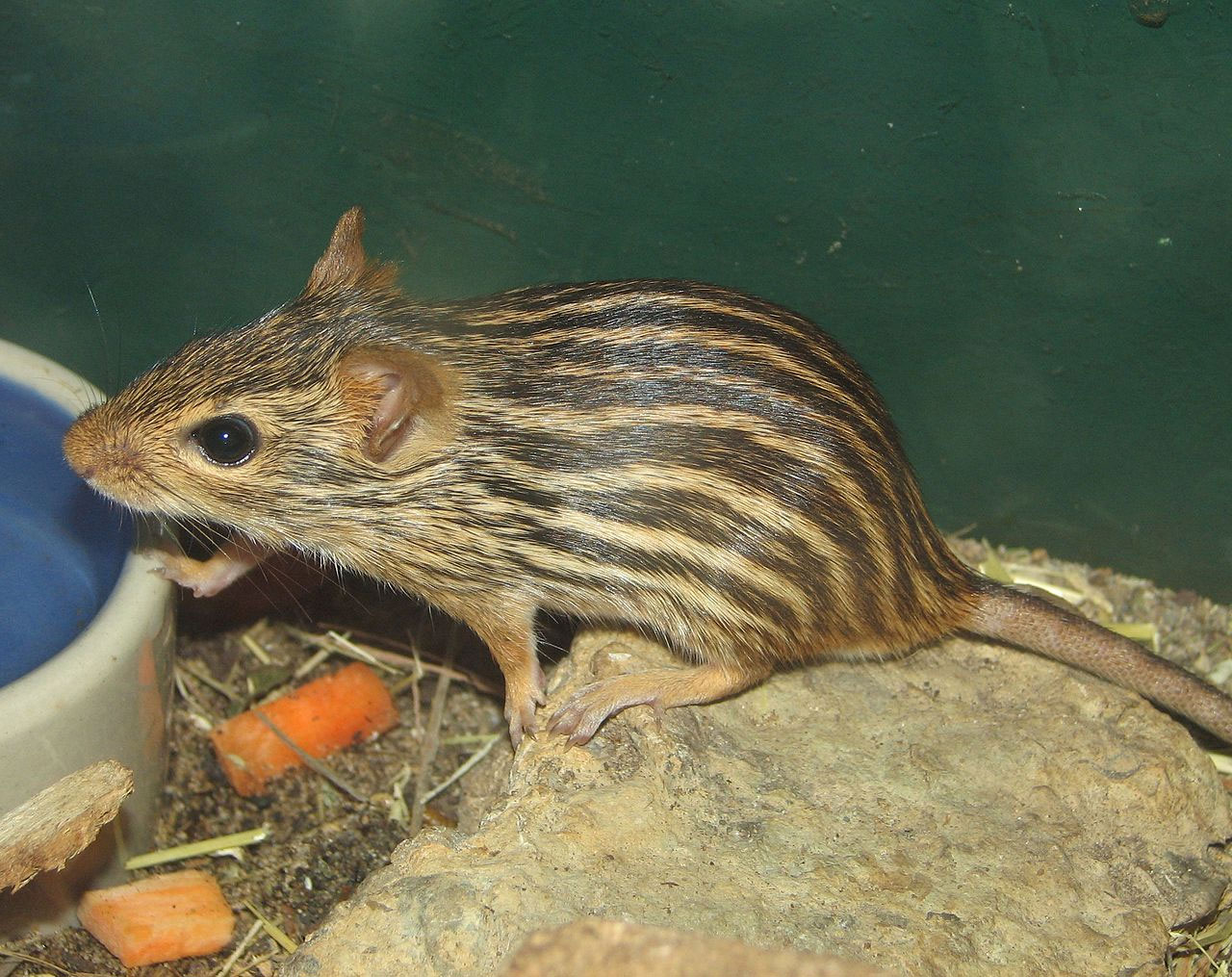
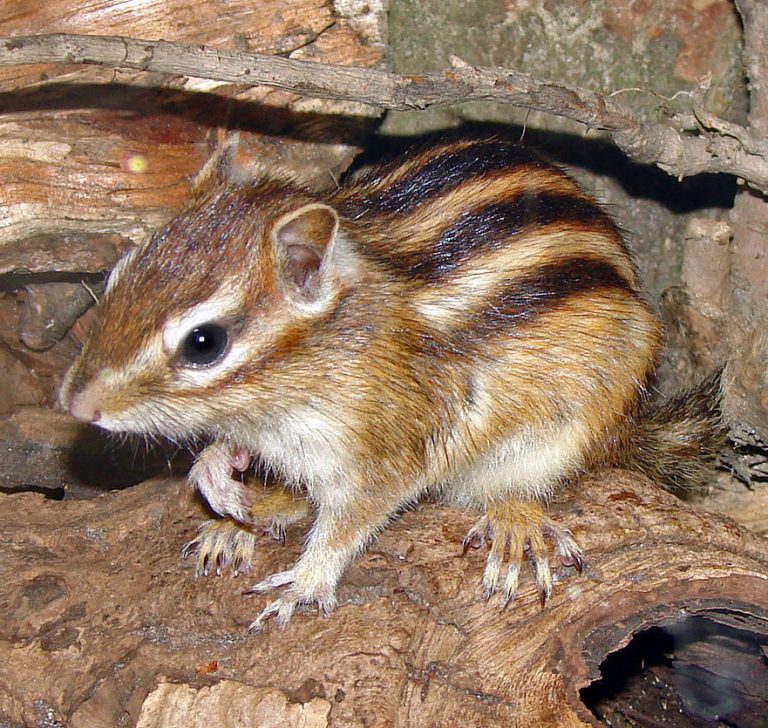
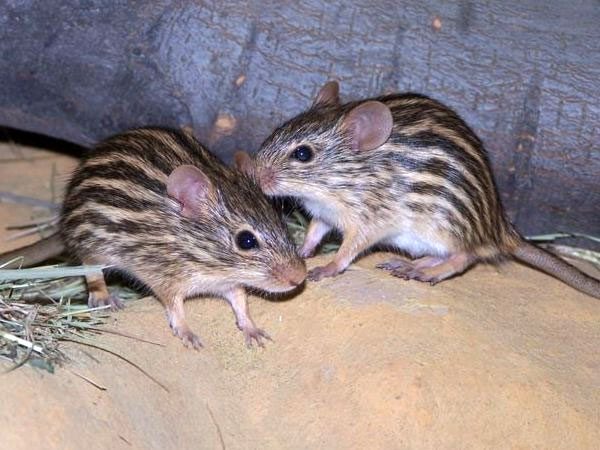
The Zebra mice belong to the genus of murine rodents hailing from Africa, at times people refer to them as the striped grass mouse. They have black stripes that extend from head to tail on their dorsal surface and either side, with a brownish body.
Anatomy
Their length ranges from 18.5 – 29 cm (7.3 – 11.4 in) almost half of which is the tail. They weigh 18 – 70 g (. 63 – 2.47 Oz). Depending on the pelage pattern, the species fall into three major groups. Distinctive dark and light striped “true zebra mice”, the dotted or more broken striped, spotted grass mice, the mice with a singular, deeply colored stripe that runs along the back called the ‘single striped grass mice’.
Behavior
The zebra mice are impossible to tame, with their occasional excitable behavior.
Habitat
These grass mice mostly occupy habitats that are grassy. You can see them all over Northern regions of Africa.
As a Pet

Breeding
By about four months time, the females mature sexually, whereas males take seven weeks. For three to five days the female stays in season and has a 21 day gestation period. Few owners succeeded in placing a female with a male at the time when she is in season, but since a few zebra mice are highly aggressive this changes with their mood. They may fight during mating and if there is any bloodshed, separate them. Once they are 14 months old, do not breed female zebra mice.
Housing
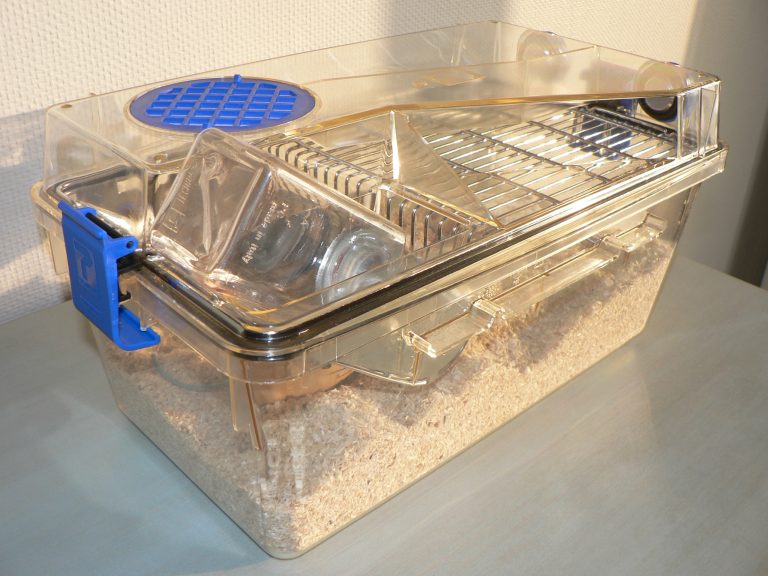
Use an aquarium or a wire cage to house zebra mice. Keep enough shavings as substrate in the cage for them to hide and nest. Use either pine shavings, Care Fresh pet bedding or aspen bedding. To make a proper environment for a zebra mouse use nest boxes or hide boxes. They love to play on exercise wheels. Keep zebra mice need warmth as they are animals of the desert. Ensure their body temperature does not fall. Place branches or twigs in their cages to climb on.
Food
Zebra mice are omnivorous which means they eat animals and plants. An assortment of fruits, vegetables, insects and seeds form an ideal diet. Pears, plums, apples or grapes are good fresh fruits. Add vegetables such as carrots, corn, sweet potatoes in their meal. Include a bit of hard-boiled eggs in their diet. Give them cooked (do not fry) and deboned, lean meat and poultry. Avoid salt, spices or sauces in such meats. Do not give processed meats. Supplement their diet with a rodent pellet available commercially.
Handling
The tail of the zebra mice is delicate and they easily shed it; so handle them gently as it does not re-grow if broken. When frightened these jumper zebra mice are capable of jumping 2 feet directly upwards. A few zebra mice adjust well to handling, but an expert in exotic rodents is best to handle them. With age, a few zebra mice grow more attached to their owners, especially on the death of cagemate.

Having discovered a fondness for insects while pursuing her degree in Biology, Randi Jones was quite bugged to know that people usually dismissed these little creatures as “creepy-crawlies”.